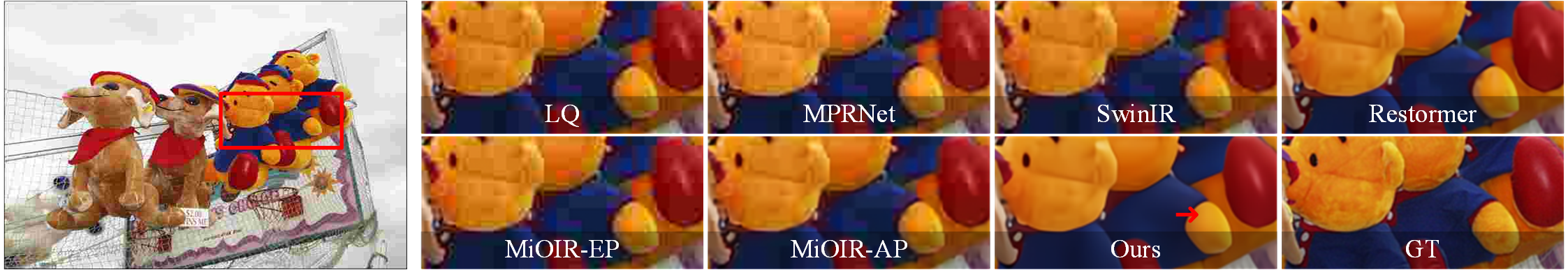
UniRestorer: Universal Image Restoration via Adaptively
Estimating Image Degradation at Proper Granularity
Jingbo Lin1Zhilu Zhang1Wenbo Li2Renjing Pei2
Hang Xu2Hongzhi Zhang1Wangmeng Zuo1
1Harbin Institute of Technology 2Huawei Noah's Ark Lab
[Paper]
[Code]
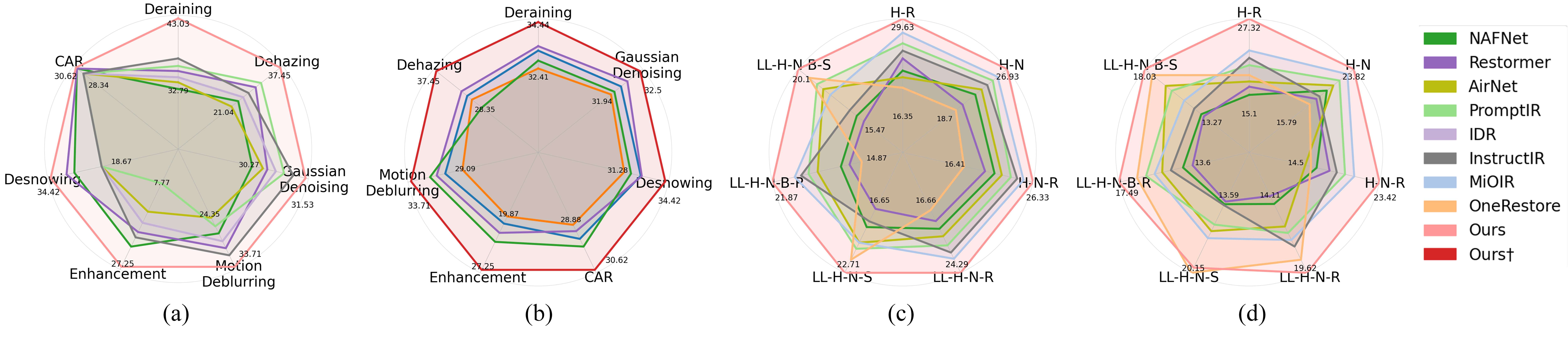
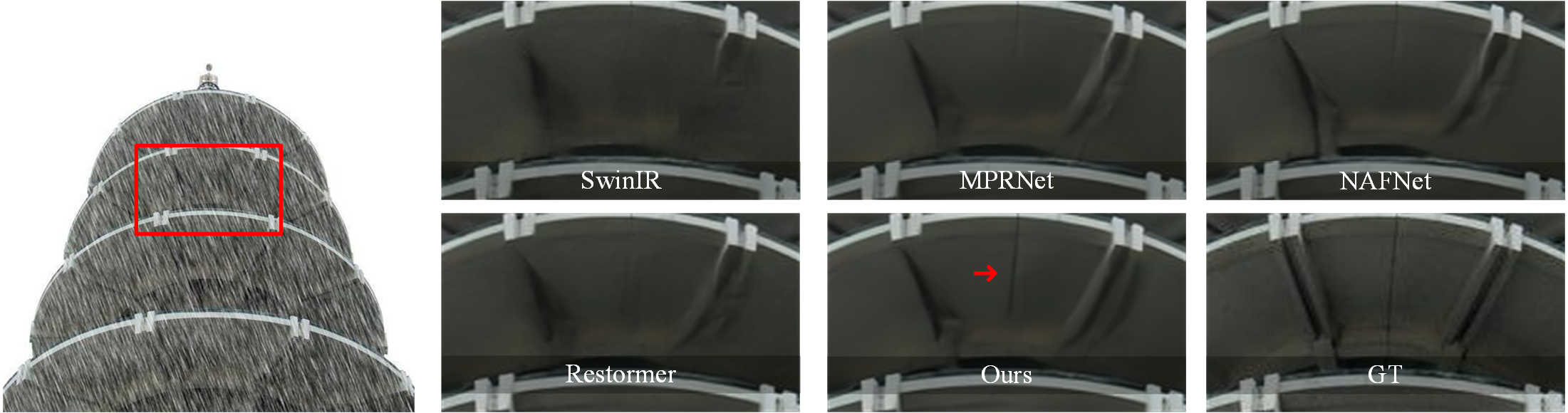
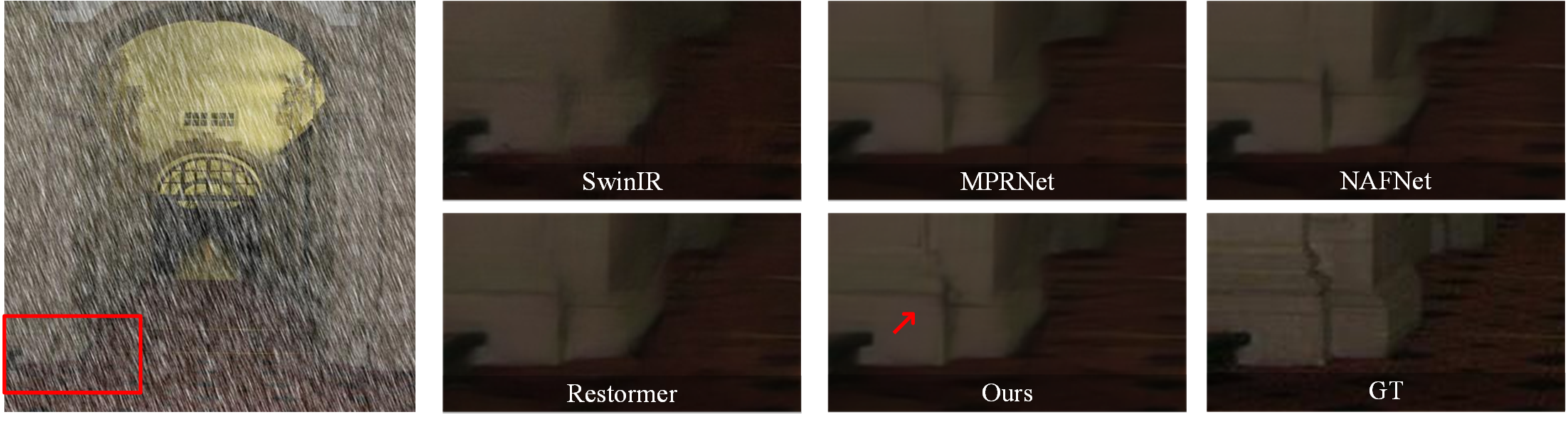
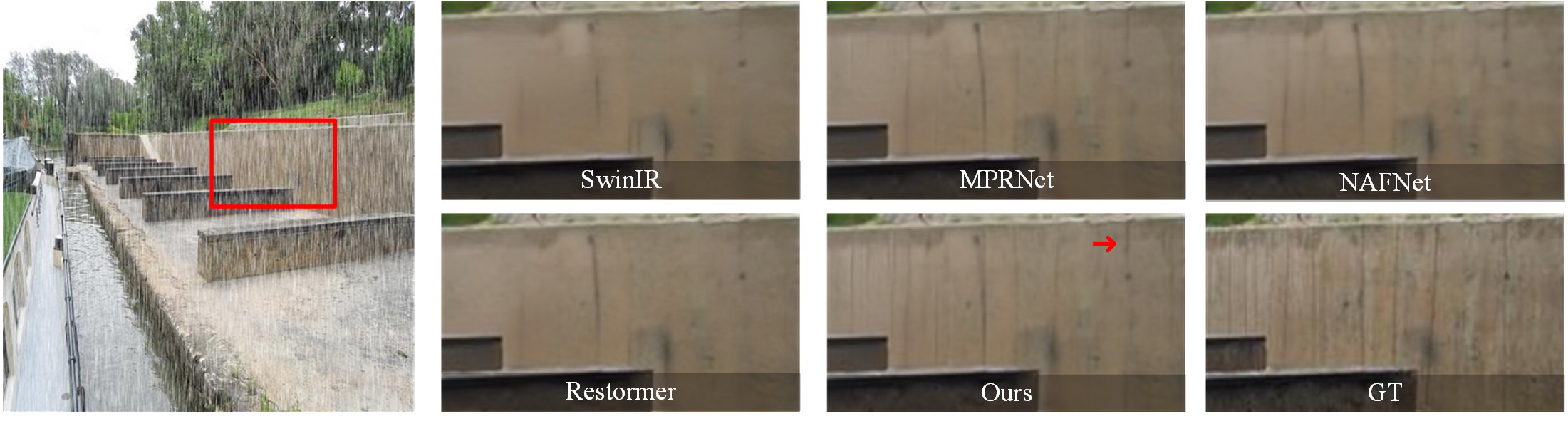
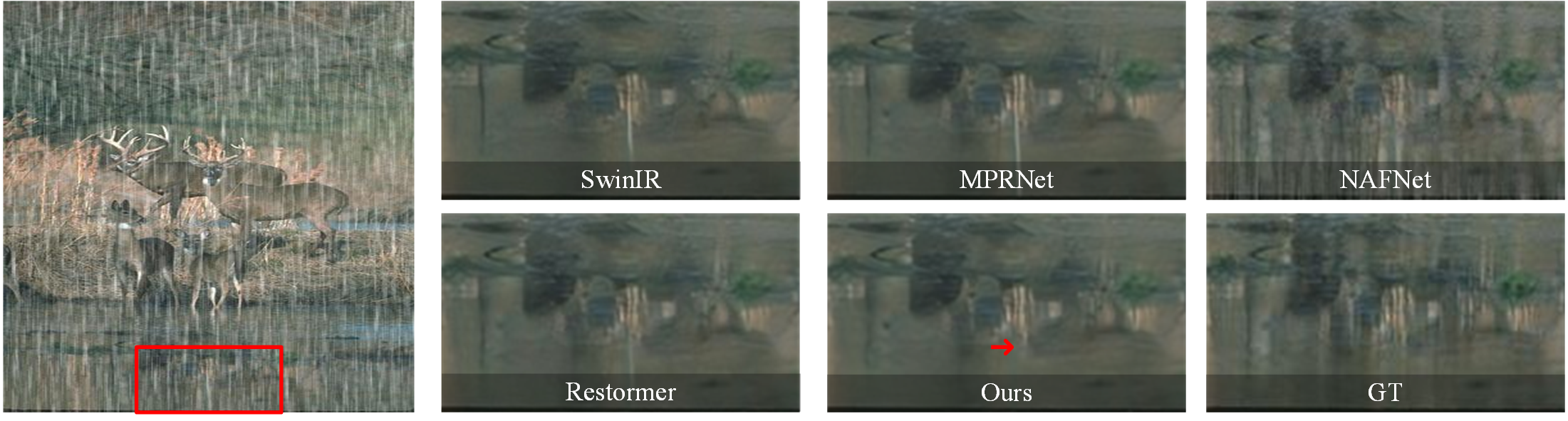
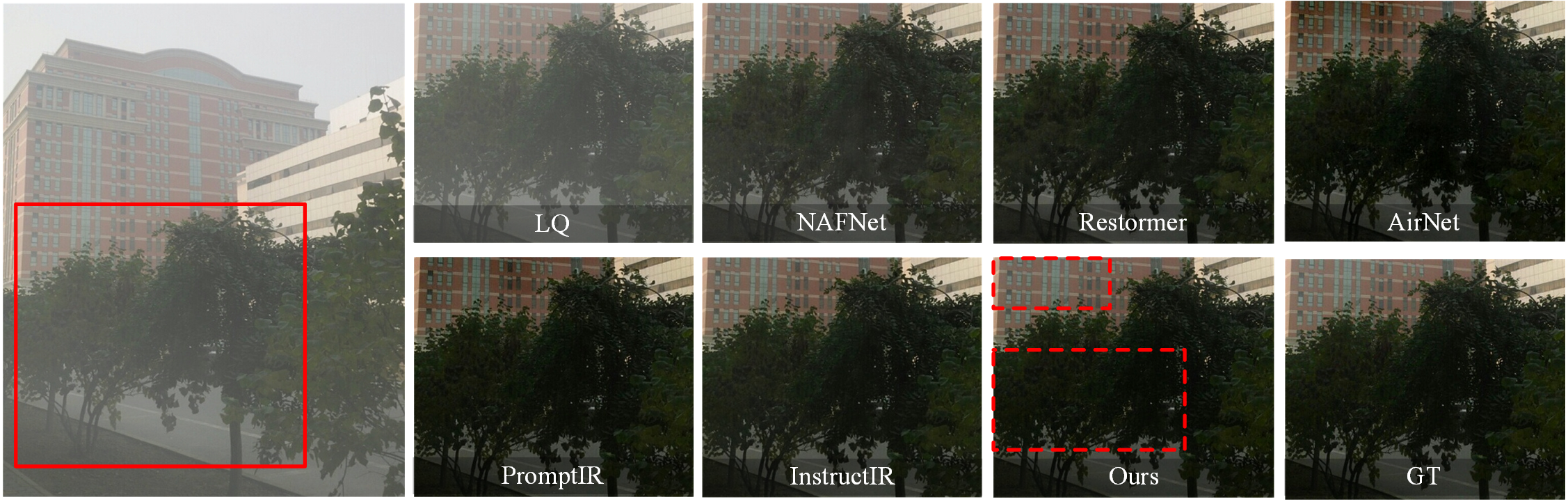
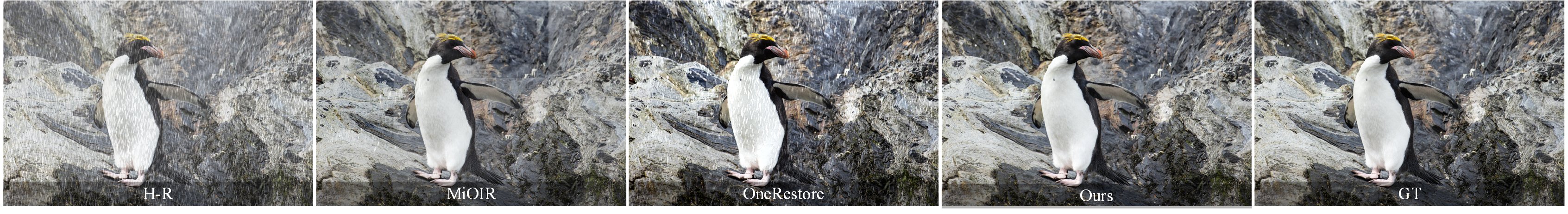
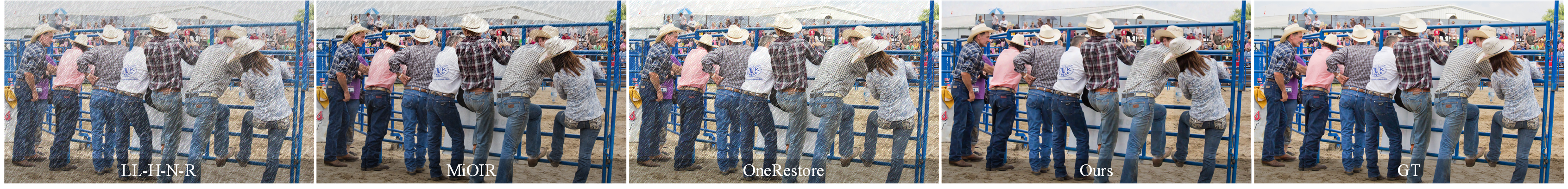
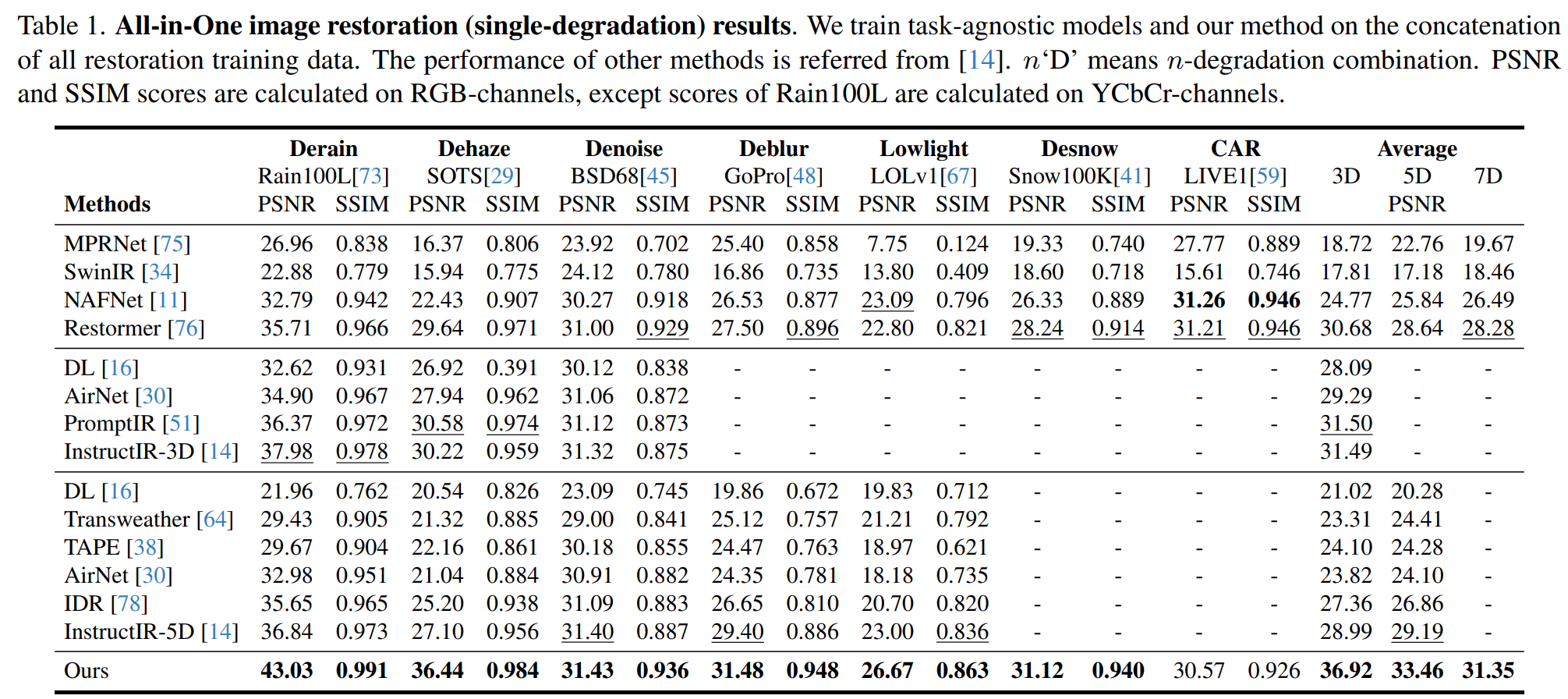
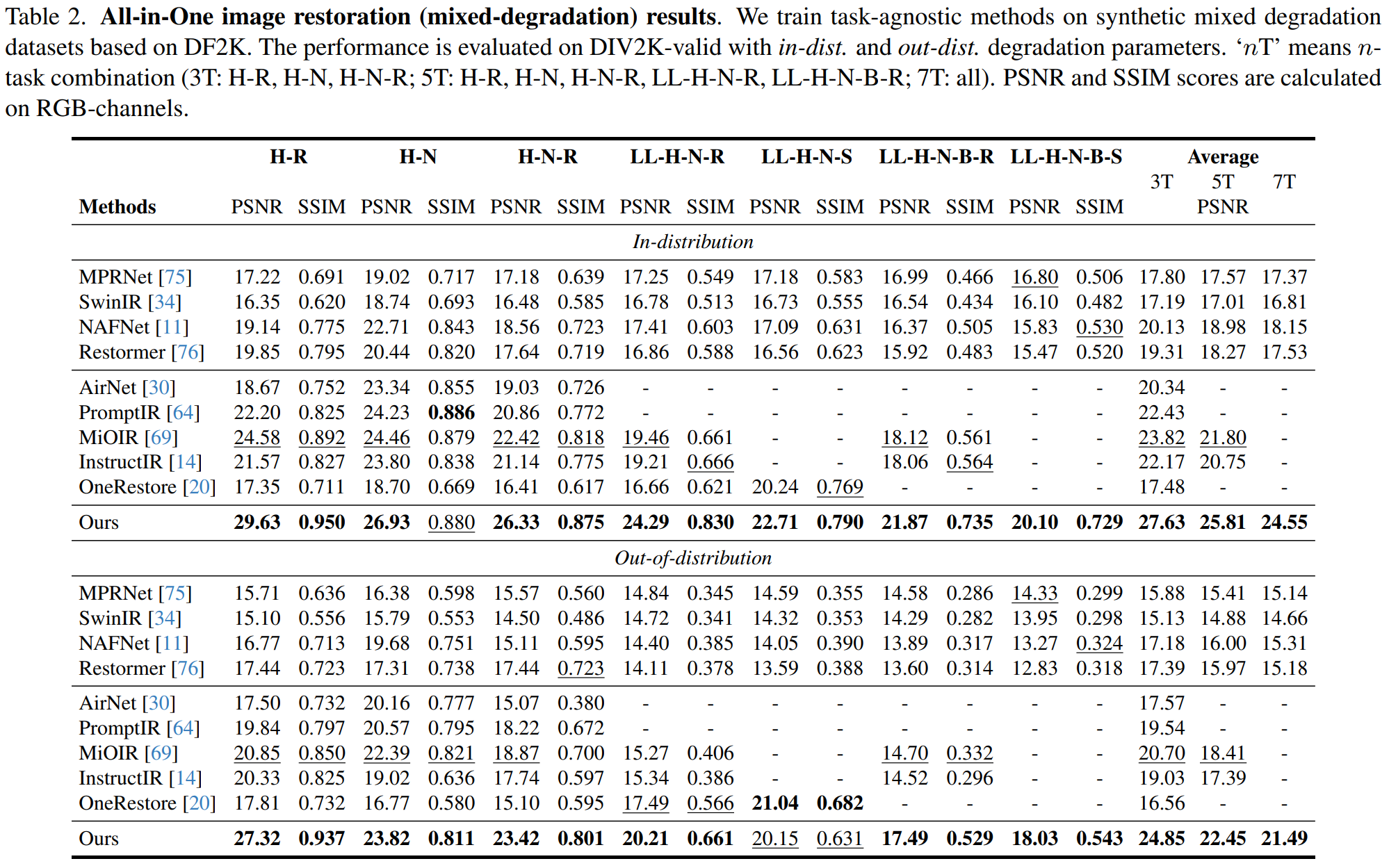
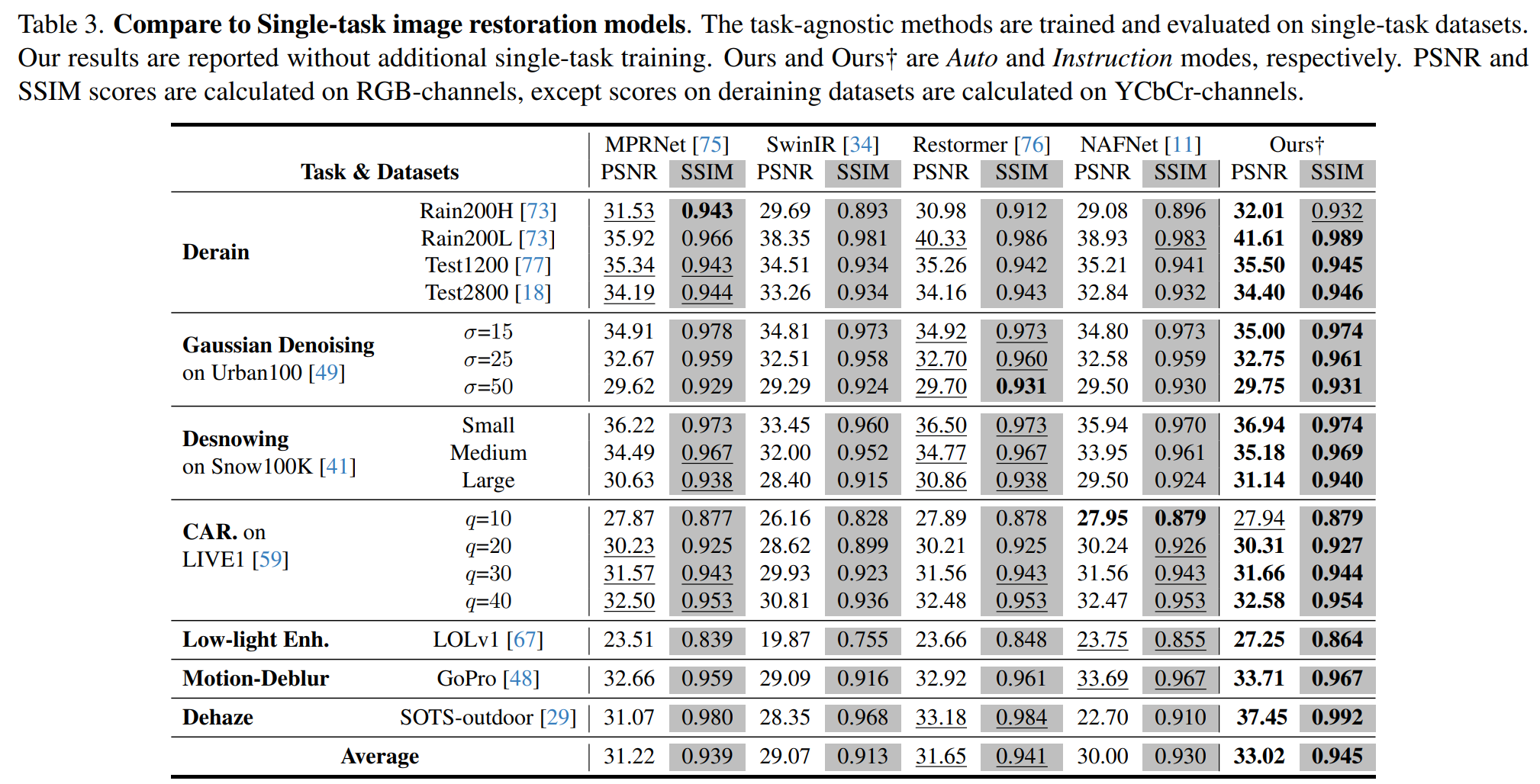
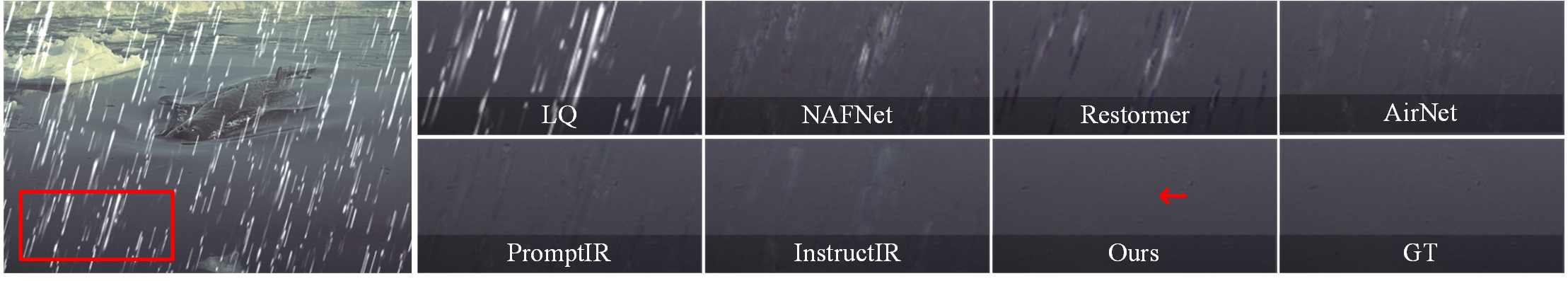
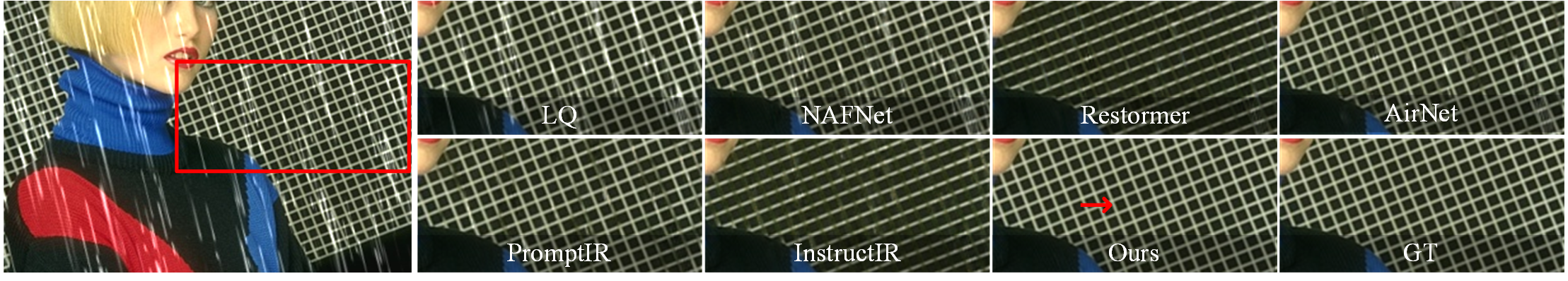
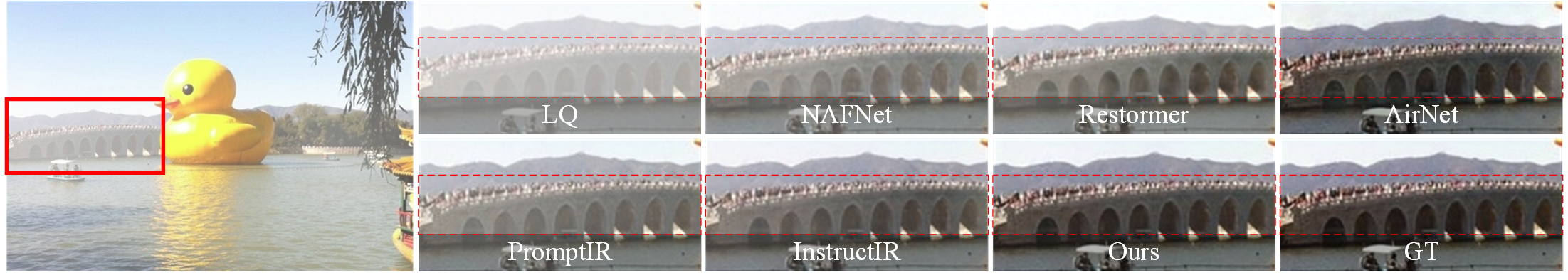
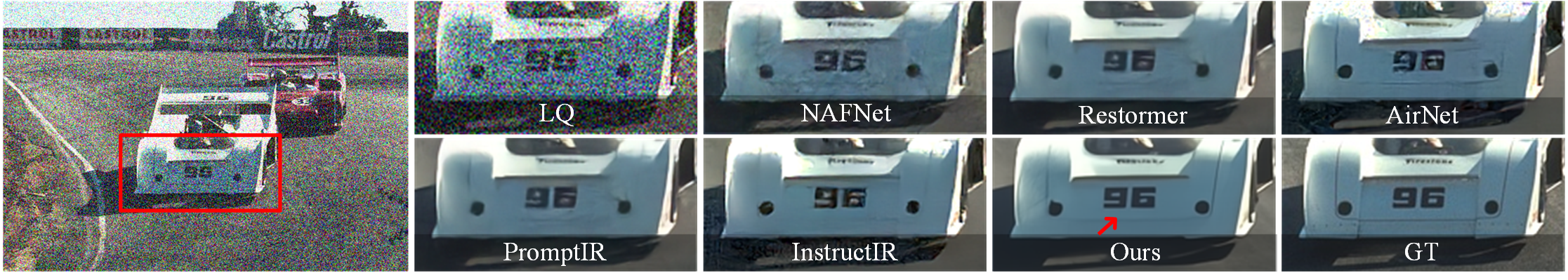
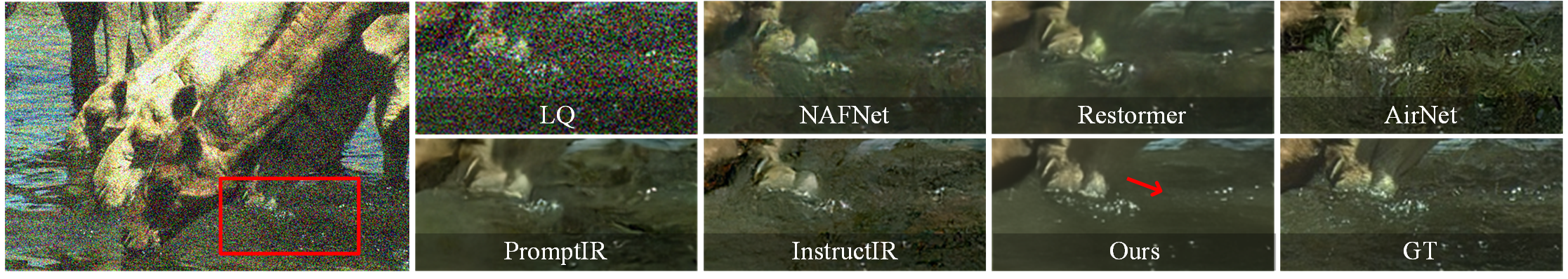
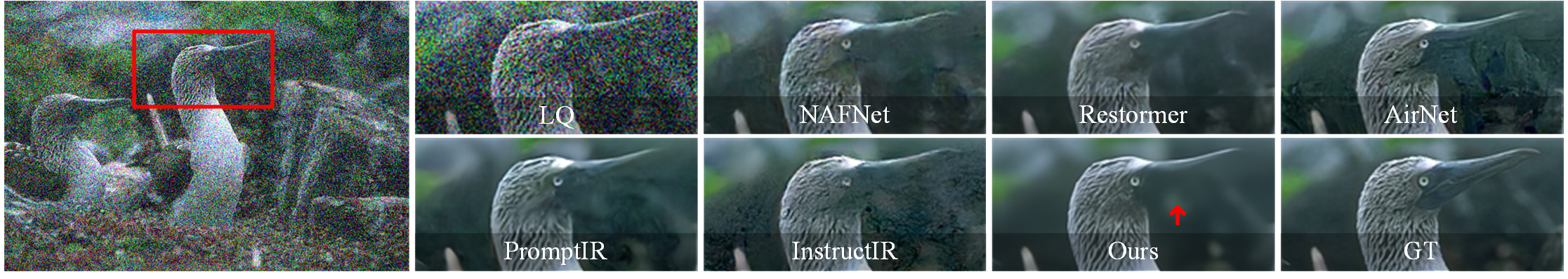
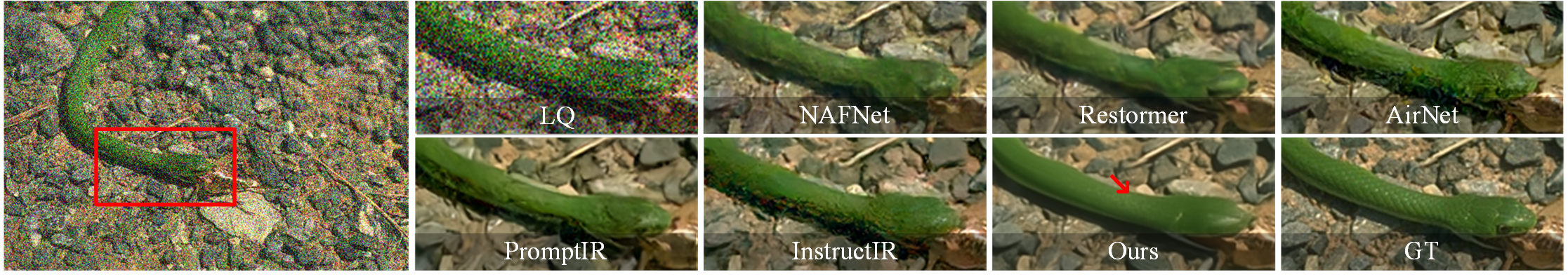
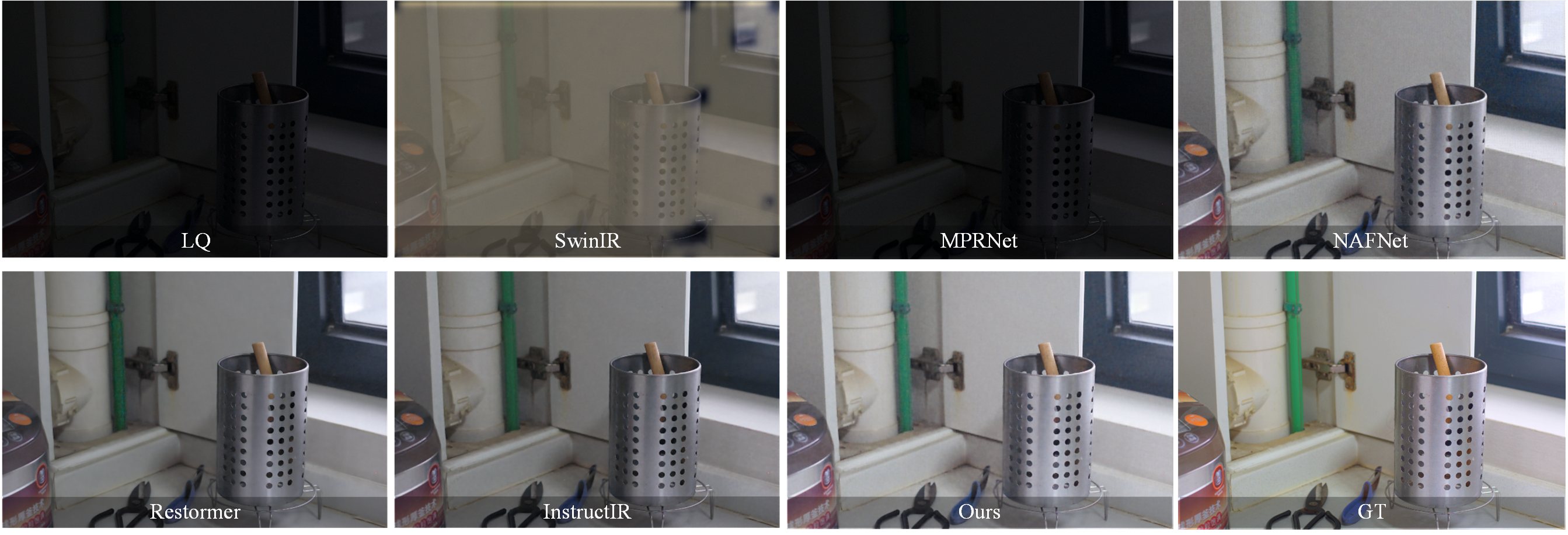
Comparisons with task-agnostic methods, all-in-one methods, and task-specific models on all-in-one image restoration.
(a) Comparisons on single-degradation setting.
(b) Comparisons with specific single-task models.
(c) Comparisons on mixed-degradation setting (in-distribution) .
(d) Comparisons on mixed-degradation setting (out-of-distribution) .
Abstract
Recently, considerable progress has been made in all-in-one image restoration.
Generally, existing methods can be degradation-agnostic or degradation-aware.
However, the former are limited in leveraging degradation-specific restoration, and the latter suffer from the inevitable error in degradation estimation.
Consequently, the performance of existing methods has a large gap compared to specific single-task models.
In this work, we make a step forward in this topic, and present our UniRestorer with improved restoration performance.
Specifically, we perform hierarchical clustering on degradation space, and train a multi-granularity mixture-of-experts (MoE) restoration model.
Then, UniRestorer adopts both degradation and granularity estimation to adaptively select an appropriate expert for image restoration.
In contrast to existing degradation-agnostic and -aware methods, UniRestorer can leverage degradation estimation to benefit degradation-specific restoration, and use granularity estimation to make the model robust to degradation estimation error.
Experimental results show that our UniRestorer outperforms state-of-the-art all-in-one methods by a large margin, and is promising in closing the performance gap to specific single-task models.
The code and pre-trained models will be publicly available.
Method
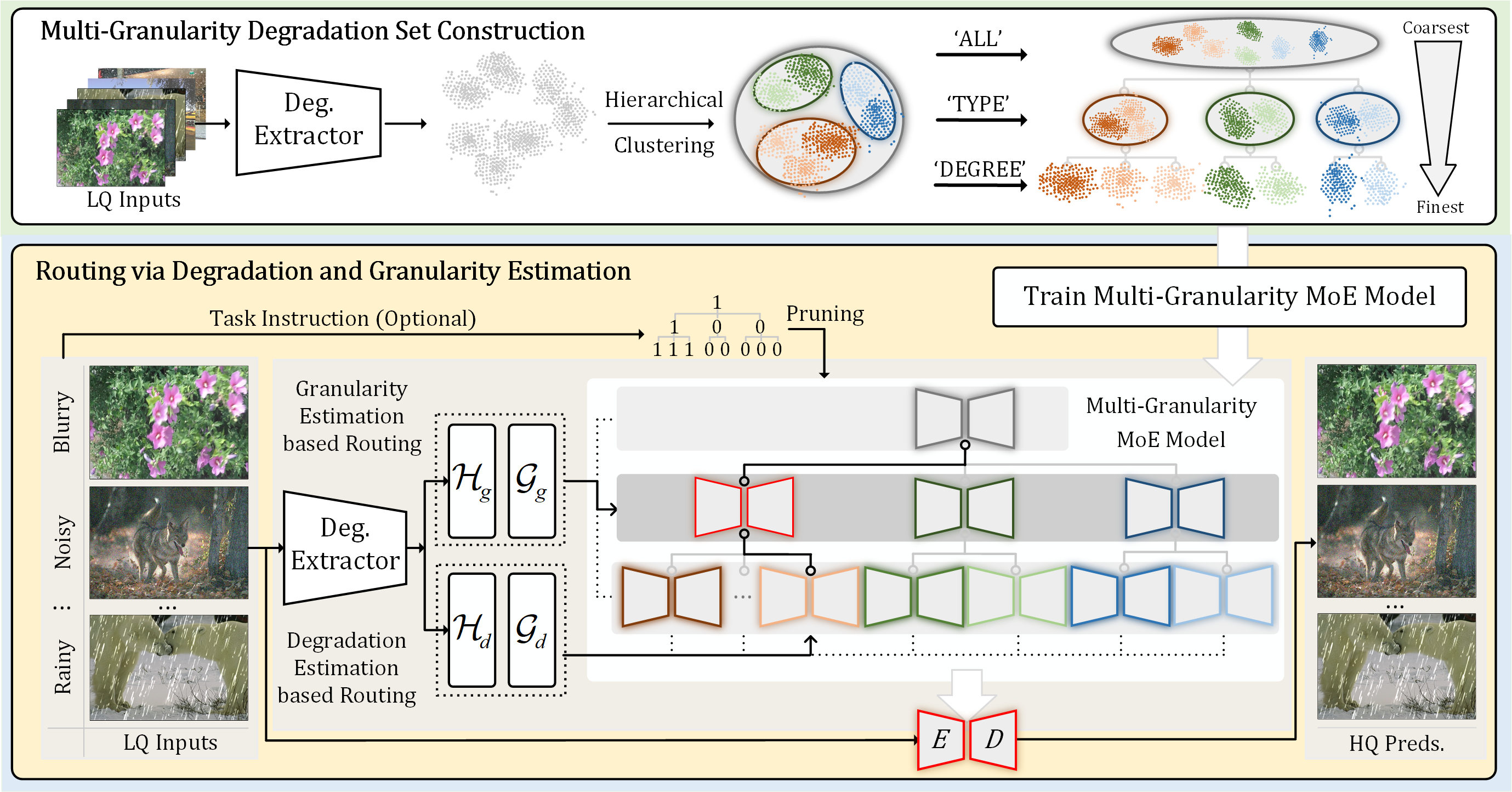
Illustration of our proposed UniRestorer.
We develop a multi-granularity degradation set by hierarchical clustering on extracted DRs at different granularity, i.e., 'ALL', 'TYPE', and 'DEGREE'.
Based on the multi-granularity degradation set, we train a multi-granularity MoE restoration model.
Besides vanilla degradation estimation, we introduce granularity estimation to indicate the degree of degradation estimation error.
Adopting both degradation and granularity estimation, we train routers to adaptively allocate an expert to unknown corrupted input.
Quantitative Comparisons
All-in-One Image Restoration (single-degradation) results, All-in-One Image Restoration (mixed-degradation) results, comparisons with single-task image restoration models.
Image Deraining
Evaluation on Rain100L dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single-degradation setting.
Comparisons with single-task models, evaluation on Rain200L, Rain200H, DID-data, and DDN-data.
Image Dehazing
Evaluation on SOTS-outdoor dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single-degradation setting.
Comparisons with single-task models, evaluation on SOTS-outdoor.
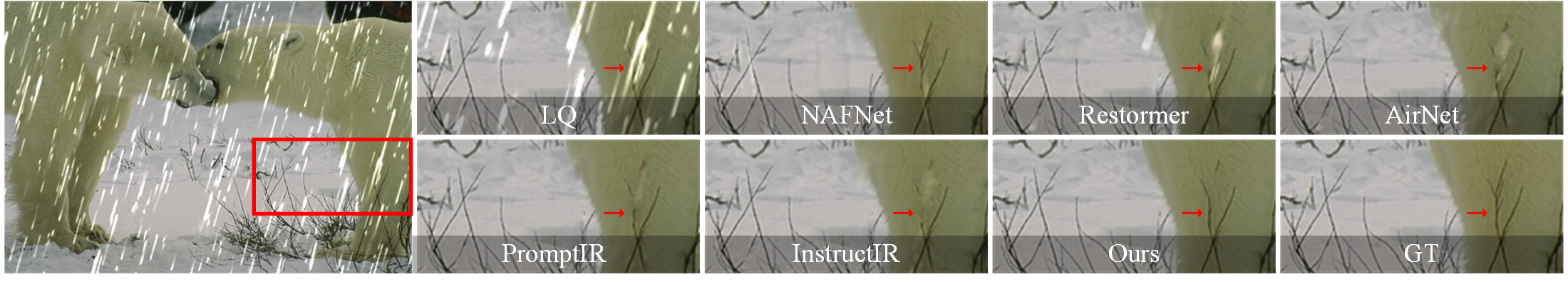
Image Desnowing
Evaluation on Snow100K-test dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single-degradation setting.
Comparisons with single-task models, evaluation on Snow100K-L, Snow100K-M, and Snow100K-S.
Gaussian Image Denoising
Evaluation on BSD68 dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single degradation setting.
Comparisons with single-task models, evaluation on Urban100 with σ=15, σ=25, and σ=50.
Motion Deblurring
Evaluation on GoPro dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single degradation setting.
Comparisons with single-task models, evaluation on GoPro.
Lowlight Enhancement
Evaluation on LOLv1 dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single degradation setting.
Compression Artifacts Removal
Evaluation on LIVE1 dataset, under All-in-One image restoration single degradation setting.
Multiple Mixed Degradation
Evaluation on Div2k-val dataset with synthetic multiple mixed degradations.
Citation
If you feel our work is helpful, you can cite our work as follows:
@article{lin2024unirestorer,
title={UniRestorer: Universal Image Restoration via Adaptively Estimating Image Degradation at Proper Granularity},
author={Lin, Jingbo and Zhang, Zhilu and Li, Wenbo and Pei, Renjing and Xu, Hang and Zhang, Hongzhi and Zuo, Wangmeng},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.20157},
year={2024}
}
If you have any question, feel free to contact
jblincs1996@gmail.com.